Prostate Cancer Treatment in Atlanta
What is Prostate Cancer?
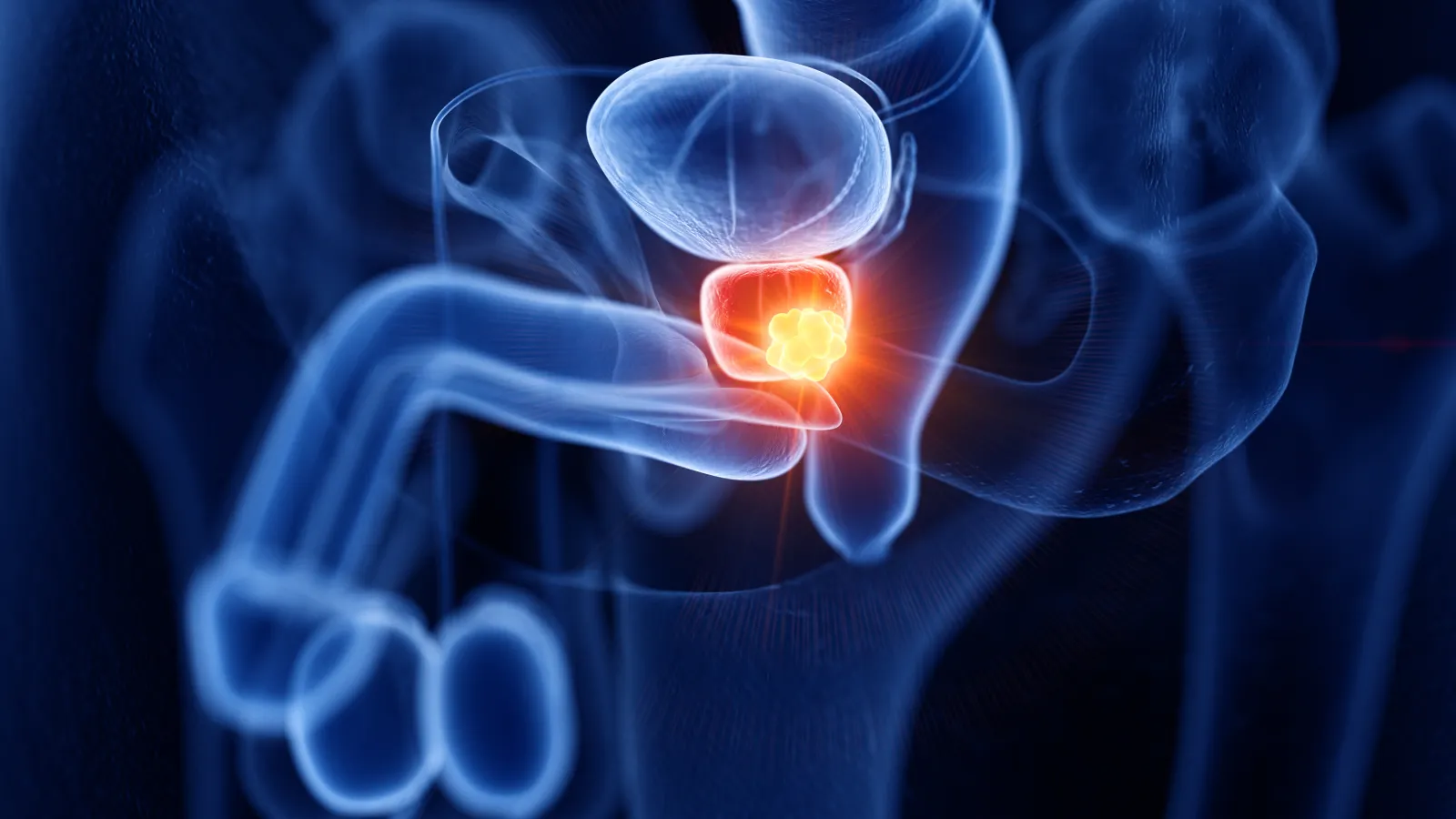
Prostate cancer is a condition where malignant cells form in the tissues of the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Early detection and treatment are crucial, and our specialists at Advanced Urology are dedicated to providing the exact care you need to manage and overcome this condition.
We Offer The Best Treatment For Prostate Cancer In Atlanta
At Advanced Urology, we offer targeted and precise therapies for localized prostate cancer, ensuring minimal sexual and urinary dysfunction, with most treatments performed as outpatient procedures in our state-of-the-art surgery centers.

Common Signs & Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Trouble urinating.
- Decreased force in the stream of urine.
- Blood in the urine.
- Blood in the semen.
- Bone pain.
- Losing weight without trying.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Swelling in the legs or feet.
- Frequent need to urinate, especially at night.
Possible Causes
Of Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown. However, doctors understand that it begins when cells in the prostate undergo changes in their DNA, which contains the instructions that control cell behavior. These changes cause the cells to grow and divide faster than normal, while abnormal cells survive when they should die. As these abnormal cells accumulate, they form a tumor that can invade surrounding tissue and, over time, some cells may spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
The PSA test measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Elevated PSA levels may indicate prostate cancer, but they can also be caused by non-cancerous conditions like prostatitis or an enlarged prostate.
A small blood sample is taken and analyzed to determine the PSA level. Normal PSA levels are generally below four nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL), but what constitutes "normal" can vary depending on age, race, and individual health. Higher levels may warrant further testing, such as imaging or a biopsy. It's a non-invasive test and can detect prostate cancer in its early stages, even before symptoms develop. It is useful for monitoring patients after prostate cancer treatment to check for recurrence.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
During a DRE, a prostate cancer doctor manually examines the prostate through the rectum to feel for abnormalities, such as lumps or hard areas, which could indicate cancer. It can detect abnormalities that might not be identified through a PSA test alone. It's quick and typically only takes a few minutes.

When to See a Doctor
If You Suspect Problems With Your Prostate
If you experience difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or pelvic discomfort, schedule an appointment with our specialists at Advanced Urology. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve your quality of life and prevent more serious health issues.
Our expert team uses advanced diagnostics to identify the underlying causes and offers personalized treatments to effectively manage your condition. Don't wait, contact Advanced Urology today for better health and comfort.
Schedule Appointment Online
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Prostate Cancer
Q Who is at risk of developing prostate cancer?
Several factors increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. Age is a significant risk factor, with the likelihood rising substantially after age 50. Family history also plays a role, as having a close relative (such as a father or brother) with prostate cancer increases the risk. African American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer, and their cases tend to be more aggressive. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as a diet high in fat and low in fruits and vegetables, as well as a lack of physical activity, may contribute to the risk.
Q Can prostate cancer be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, certain lifestyle changes may reduce your risk. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying physically active, and maintaining a healthy weight can help. Additionally, regular screenings and discussions with a prostate cancer specialist about your risk factors can aid in early detection and prevention.
Q What is Prostate Cancer TNM Staging?
The TNM staging system is a standardized method used by doctors to describe the extent and severity of prostate cancer. TNM stands for Tumor (T), Nodes (N), and Metastasis (M), and it helps guide treatment decisions and predict outcomes.
Q Is prostate cancer hereditary?
Yes, prostate cancer can run in families. Having a close relative, such as a father, brother, or son, with prostate cancer increases your risk of developing the disease. Additionally, inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, or HOXB13, may also raise the likelihood of prostate cancer. If you have a family history of prostate cancer or related cancers (such as breast or ovarian cancer), it is important to inform your doctor, as they may recommend earlier or more frequent screenings.